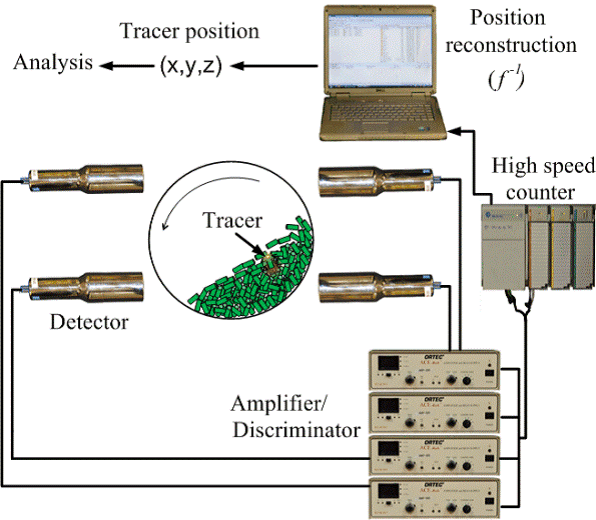
Single/Multiple Radioactive Particle Tracking (RPT)
The RPT noninvasively tracks the position of a single radioactive tracer over time and can thus be used to study the flow dynamics of a variety of systems. A labeled tracer particle, a data acquisition system (detectors, amplifiers/discriminators, and high-speed counters), and a location algorithm are used to calculate the position of the tracer as shown in the figure for granular flows in a rotating drum.
M. Rasouli et al. AIChE J. 2015; 61(2); 384-394
The MRPT technique simultaneously tracks two tracers that move freely (free MRPT) or that remain at a fixed distance from each other (restricted MRPT), it uses the same basic setup as RPT, with two main differences. First, it uses two radioactive sources with the same isotope that are inserted into two different tracer particles (free MRPT) or into a single tracer particle (restricted MRPT; at both ends of a single cylindrical particle). Second, it uses a different location algorithm since the gamma rays measured by the acquisition system come from two different radioactive sources.